Do i have bladder cancer quiz – Do I Have Bladder Cancer? Take Our Quiz to Find Out. If you’re experiencing symptoms such as frequent urination, pain during urination, or blood in your urine, you may be wondering if you have bladder cancer. This quiz can help you assess your risk and determine if you should see a doctor.
Bladder cancer is a serious disease, but it’s often curable if it’s caught early. That’s why it’s important to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors, and to get regular checkups if you’re at high risk.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
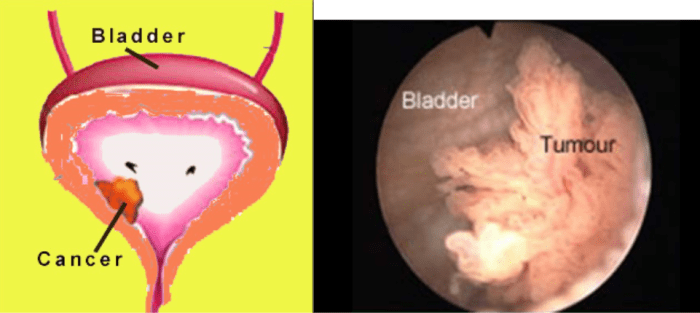
Bladder cancer is a serious condition that can affect both men and women. While early detection is key to successful treatment, many people may not experience any symptoms in the early stages of the disease.
As the cancer progresses, however, several common symptoms may manifest:
Blood in the Urine
- One of the most common signs of bladder cancer is the presence of blood in the urine (hematuria). This can range from visible blood clots to microscopic amounts detectable only through a urine analysis.
- Hematuria can be painless and intermittent, making it easy to ignore. However, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately if you notice any blood in your urine, even if it appears to go away on its own.
Frequent Urination
- Another common symptom is the need to urinate frequently, especially at night (nocturia).
- This can be caused by the tumor irritating the bladder, leading to an increased urge to urinate.
Painful Urination
- Bladder cancer can also cause pain or burning during urination (dysuria).
- This pain may be caused by the tumor blocking the flow of urine or by inflammation of the bladder lining.
Other Symptoms
- In some cases, bladder cancer may also cause other symptoms, such as:
- Lower back pain
- Pelvic pain
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to these symptoms, there are certain risk factors that can increase your chances of developing bladder cancer:
Risk Factors
- Smoking:Smoking is the leading risk factor for bladder cancer, as it exposes the bladder to harmful chemicals.
- Occupational exposure to certain chemicals:People who work with certain chemicals, such as aromatic amines and certain dyes, have an increased risk of bladder cancer.
- Previous radiation therapy:People who have undergone radiation therapy to the pelvic area are at an increased risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Chronic bladder infections:People with a history of chronic bladder infections may have an increased risk of bladder cancer.
- Age:The risk of bladder cancer increases with age.
- Gender:Men are more likely to develop bladder cancer than women.
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment of bladder cancer. Regular check-ups, including urinalysis and cystoscopy, can help detect bladder cancer in its early stages, when it is most treatable.
If you’re wondering if you might have bladder cancer, you’ll want to check out the dat bootcamp high yield notes . They’ve got a great quiz that can help you assess your risk. It’s quick and easy to take, and it could give you some peace of mind.
Diagnostic Procedures: Do I Have Bladder Cancer Quiz

To accurately diagnose bladder cancer, several diagnostic tests are employed. These tests provide valuable information about the presence, location, and stage of the cancer.
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a procedure that involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached into the urethra and bladder. This allows the doctor to visualize the inside of the bladder and identify any abnormal growths or lesions.
Urine Cytology
Urine cytology is a test that examines cells shed from the bladder and present in the urine. A sample of urine is collected and analyzed under a microscope to detect any abnormal cells that may indicate the presence of bladder cancer.
Biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from the bladder for further examination. This tissue sample is then analyzed under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis of bladder cancer and determine its type and stage.
These diagnostic tests play a crucial role in detecting bladder cancer and providing valuable information for treatment planning.
Treatment Options
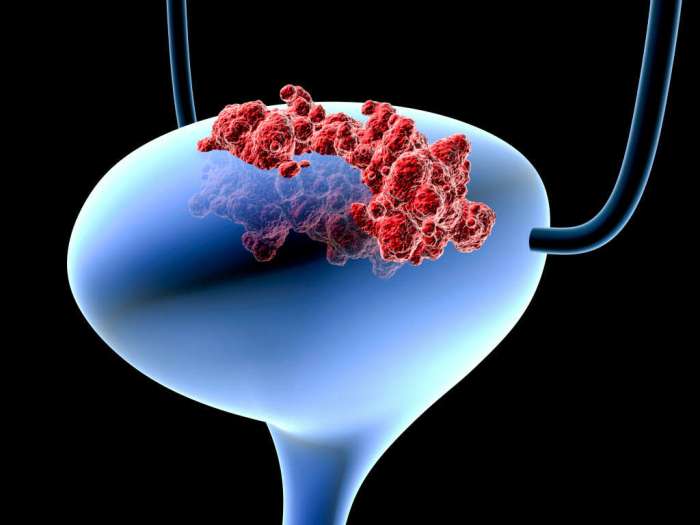
Bladder cancer treatment depends on the stage and grade of the cancer. Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these.
Surgery, Do i have bladder cancer quiz
- Transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT):This is a minimally invasive procedure that removes the tumor through the urethra.
- Partial cystectomy:This surgery removes part of the bladder.
- Radical cystectomy:This surgery removes the entire bladder and nearby lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be given orally, intravenously, or directly into the bladder.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It can be given externally or internally (brachytherapy).
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. It can be given as a vaccine, antibody, or cytokine.
Prevention and Management
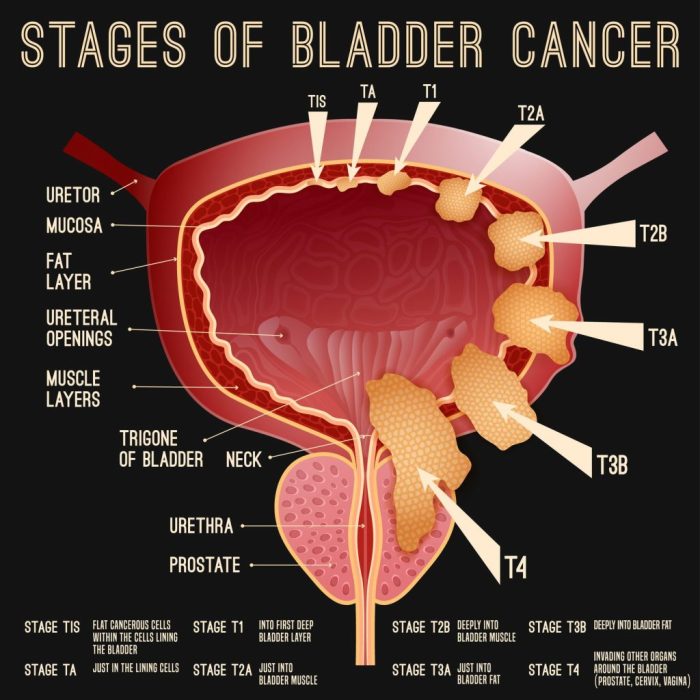
Adopting a proactive approach to bladder cancer prevention and management is crucial. Understanding the risk factors and implementing lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this condition. Additionally, managing symptoms and maintaining a positive outlook can improve the quality of life for individuals with bladder cancer.
Risk Reduction Strategies
- Cessation of Smoking:Smoking is a major risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking is the single most effective way to reduce the risk.
- Hydration:Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps dilute urine and flush out potential carcinogens.
- Healthy Diet:Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help protect against bladder cancer.
- Occupational Safety:Exposure to certain chemicals in the workplace, such as aromatic amines, can increase the risk. Employers must provide adequate safety measures.
Symptom Management
Bladder cancer symptoms can impact daily life. Effective management strategies can alleviate discomfort and improve well-being.
- Medication:Medications can help control pain, reduce urinary frequency, and prevent infection.
- Lifestyle Modifications:Dietary changes, such as limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, can reduce bladder irritation.
li> Bladder Training:Exercises can help strengthen the bladder muscles and improve urinary control.
Emotional and Social Support
Bladder cancer can have a significant emotional impact. Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups can provide comfort and reduce stress.
- Counseling:Professional counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of bladder cancer.
- Support Groups:Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- Mindfulness Techniques:Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most common symptoms of bladder cancer include frequent urination, pain during urination, and blood in the urine.
What are the risk factors for bladder cancer?
The risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, and a family history of the disease.
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
Bladder cancer is diagnosed through a combination of tests, including a physical exam, urine cytology, and cystoscopy.
How is bladder cancer treated?
The treatment for bladder cancer depends on the stage of the disease. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy.