Minstrel manufacturing uses a job order – Minstrel manufacturing, a sector renowned for its intricate craftsmanship and bespoke creations, has strategically adopted a job order costing system. This accounting method serves as a cornerstone for effective cost management, enabling manufacturers to accurately track and allocate expenses associated with each unique production order.
By implementing a job order costing system, minstrel manufacturers gain unparalleled visibility into their production processes, empowering them to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall profitability.
Job Order Costing System

Job order costing is a costing method that assigns costs to specific job orders. It is relevant to minstrel manufacturing because it allows manufacturers to track the costs associated with each individual order, which is essential for pricing and profitability analysis.
Examples of how job order costing is used in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Tracking the costs of materials used to produce a specific order.
- Tracking the costs of labor hours spent on a specific order.
- Tracking the costs of overhead expenses allocated to a specific order.
Advantages of using a job order costing system in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Improved cost control.
- Enhanced profitability analysis.
- Better decision-making.
Disadvantages of using a job order costing system in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Can be complex and time-consuming.
- Requires accurate data collection.
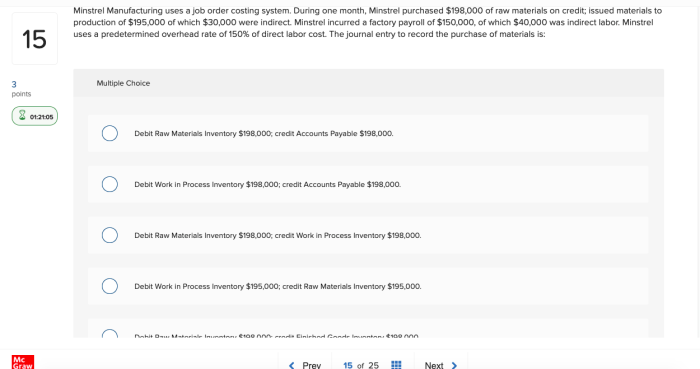
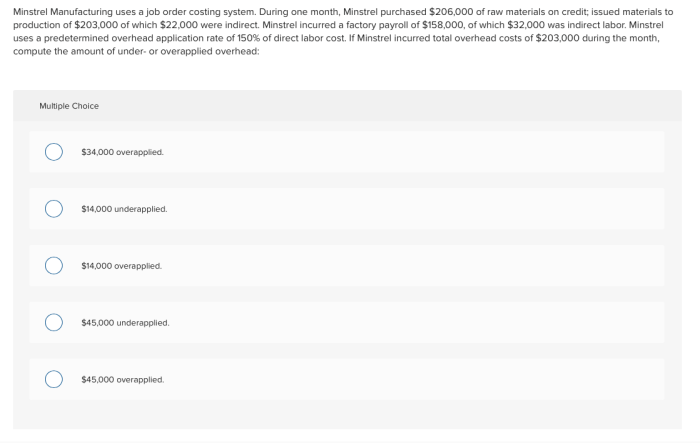
- May not be suitable for all types of manufacturing.
Production Process
The production process of minstrel manufacturing involves the following key steps:
- Raw material procurement:Acquiring the necessary raw materials, such as wood, metal, and fabric.
- Cutting and shaping:Using tools and machinery to cut and shape the raw materials into the desired components.
- Assembly:Putting together the components to create the finished product.
- Finishing:Applying the final touches, such as painting or polishing, to the finished product.
- Quality control:Inspecting the finished product to ensure it meets the required standards.
Challenges and opportunities associated with each step of the production process include:
- Raw material procurement:Ensuring the availability of high-quality raw materials at a reasonable cost.
- Cutting and shaping:Optimizing the cutting and shaping process to minimize waste and improve efficiency.
- Assembly:Ensuring the accuracy and precision of the assembly process to produce high-quality products.
- Finishing:Achieving the desired finish while maintaining the product’s integrity.
- Quality control:Implementing effective quality control measures to identify and correct any defects.
Cost Allocation
Costs are allocated to specific job orders in minstrel manufacturing using various methods, including:
- Direct costing:Assigning costs that can be directly traced to a specific job order.
- Indirect costing:Allocating costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific job order, such as overhead expenses.
- Activity-based costing:Assigning costs based on the activities performed to produce a specific job order.
The appropriateness of each cost allocation method depends on the specific circumstances of the minstrel manufacturing operation.
Accurate cost allocation is important in minstrel manufacturing because it allows manufacturers to:
- Determine the profitability of individual job orders.
- Identify areas for cost reduction.
- Make informed pricing decisions.
Inventory Management
Inventory management in minstrel manufacturing involves managing the flow of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
Types of inventory held by minstrel manufacturers include:
- Raw materials:Materials used to produce minstrel products.
- Work-in-progress:Partially completed minstrel products.
- Finished goods:Completed minstrel products ready for sale.
Challenges and opportunities associated with inventory management in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Raw materials inventory:Ensuring the availability of raw materials while minimizing waste.
- Work-in-progress inventory:Managing the flow of work-in-progress to avoid bottlenecks and delays.
- Finished goods inventory:Optimizing finished goods inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing storage costs.
Job Costing Reports
Job costing reports provide information about the costs associated with specific job orders.
Types of job costing reports used in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Job cost sheets:Summarize the costs incurred on a specific job order.
- Job profitability reports:Show the profitability of individual job orders.
- Job cost analysis reports:Provide detailed information about the costs associated with a specific job order.
Job costing reports are important for decision-making in minstrel manufacturing because they provide information about:
- The profitability of individual job orders.
- The efficiency of the production process.
- Areas for cost reduction.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a process of ongoing improvement in minstrel manufacturing operations.
Methods used for continuous improvement in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Kaizen:A Japanese philosophy that focuses on continuous improvement through small, incremental changes.
- Lean manufacturing:A production philosophy that focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency.
- Six Sigma:A quality management methodology that focuses on reducing defects and improving quality.
Benefits and challenges of implementing continuous improvement in minstrel manufacturing include:
- Benefits:Improved quality, reduced costs, increased efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Challenges:Requires commitment from all levels of the organization, can be time-consuming, and may require significant investment.
Q&A: Minstrel Manufacturing Uses A Job Order
What are the key advantages of using a job order costing system in minstrel manufacturing?
Job order costing provides precise cost tracking for each production order, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for cost reduction, improve pricing strategies, and enhance profitability.
How does cost allocation impact the accuracy of job costing reports?
Accurate cost allocation is crucial for reliable job costing reports. By assigning costs to specific job orders based on appropriate allocation methods, manufacturers can ensure that each product bears its fair share of expenses.
What role does inventory management play in job order costing for minstrel manufacturing?
Effective inventory management ensures that raw materials and components are available when needed for production. This helps minimize production delays, reduce waste, and improve overall cost control.